
Ø Proteins in their functional, folded conformations are called native proteins. Ø The spatial arrangement of atoms in a protein is called its ‘ Conformation’. Ø This unique structural formation of a protein is called its 3D structure. Ø However, each protein has a specific (unique) structural conformation. Ø The free rotation allows an unlimited number of conformations around these bonds. Ø Free rotation is possible around many of these bonds. Ø The backbone of a protein contains hundreds of individual bonds. Ø Primary structure data can be used for the sequence searching from the protein databases. Ø The primary structure of a protein will offer insights into its: Ø First sequenced protein: Insulin by Frederick Sanger. Ø The first study about an unknown protein will be its sequence determination (determination of primary structure). Ø The primary structure is stabilized by Peptide Bonds ( Covalent Bond). Ø The primary structure of a protein will determine all other levels of structural organization of a protein (secondary, tertiary and quaternary). Ø The ‘sequence’ information contains the correct order of amino acids in the protein starting from N-terminal to C-terminal. BIOLOGY ZOOLOGY MICROBIOLOGY BIOSTATISTICS ECOLOGY IMMUNOLOGY BIOTECHNOLOGY GENETICS EMBRYOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY EVOLUTION BIOPHYSICS BIOINFORMATICS
/protein-structure-373563_final11-5c81967f46e0fb00012c667d.png)
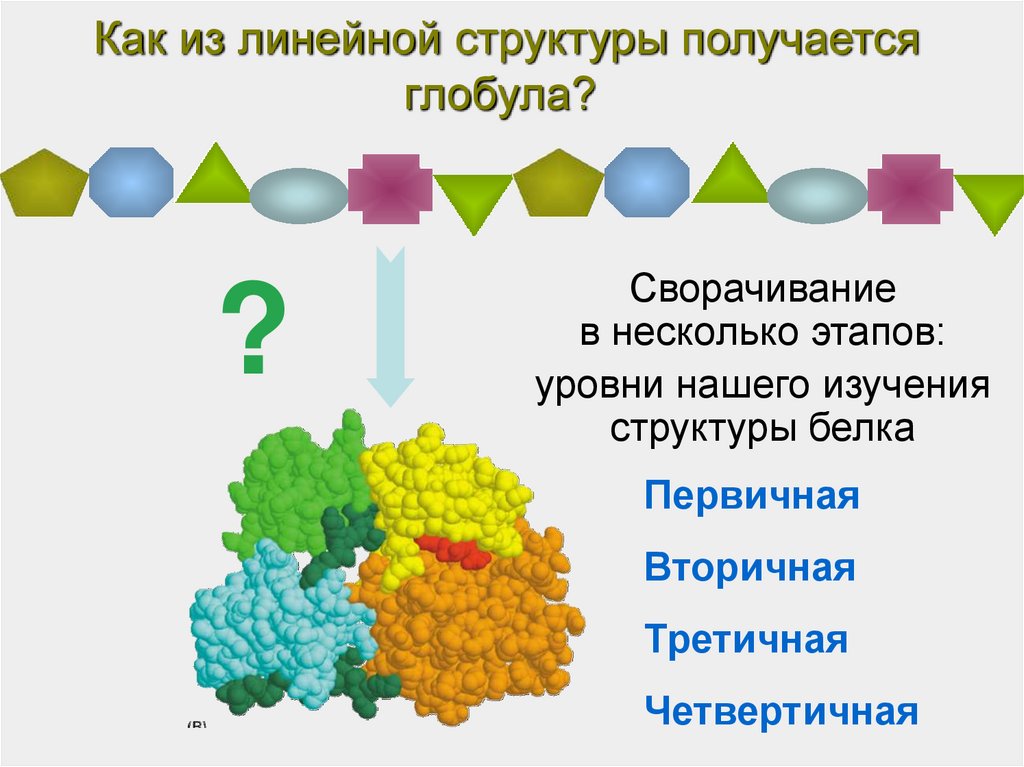
Ø The primary structure will tell you two main things: (i) The number of amino acid residues in the protein and (ii) the sequence of amino acids. Ø Primary structure of a protein gives the details of the amino acid sequence of a protein. Ø Some proteins will have all the 4 levels of structures (up to quaternary structure). Ø All functional proteins will have up to 3 (tertiary level) of structures. Ø Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary structure are together called the three-dimensional (3D) structure of the protein.įacts About Proteins and Protein Structure

Ø A protein can have Four levels of structural organization: In the present post, we will discuss different types of protein structures. Previously we have discussed but the ‘ Bonds involved in Protein Structure”. A protein can have up to four levels of structural conformations. This linear polypeptide chain is folded into specific structural conformations or simply ‘ structure’.
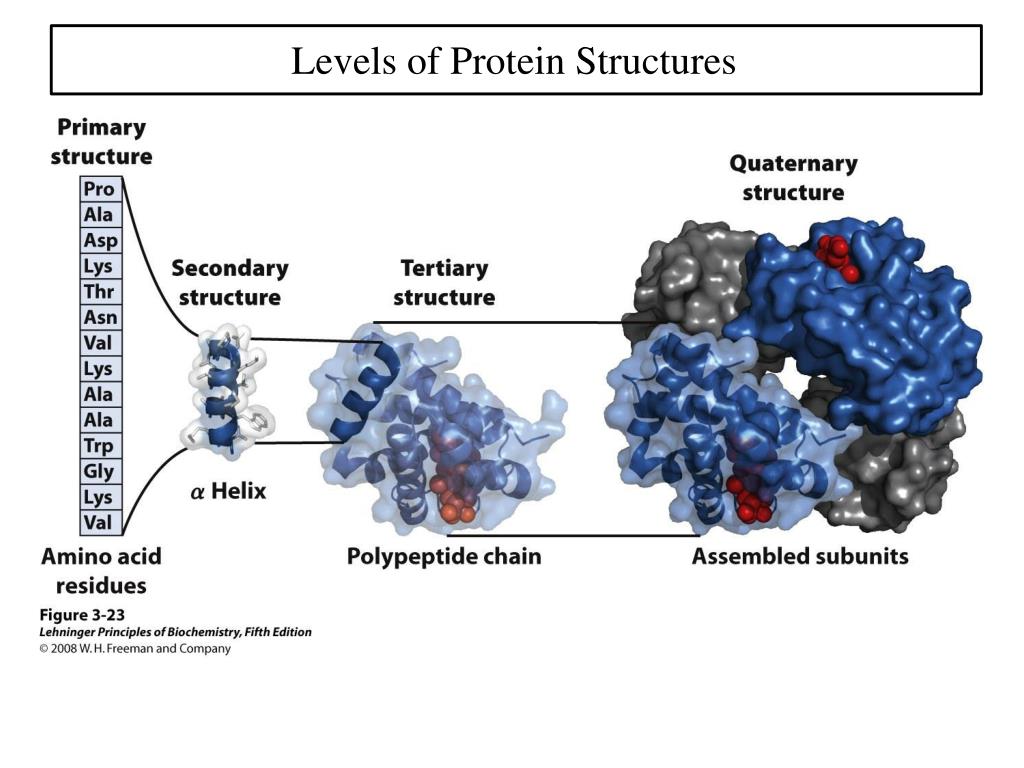
Individual amino acids (residues) are joined by peptide bonds to form the linear polypeptide chain. Ø Proteins are the polymers of amino acids. Learning objectives Structure of Proteins: Protein Structure: Primary Structure, Secondary Structure (Alpha Helix, Beta Plates, Beta Turns), Tertiary Structure, Quaternary Structure, Bonds Stabilizing different Protein Structures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
